Turtle or Tortoise? How to Tell the Two Apart
What is the difference between turtle and tortoise? Turtles typically spend more time in water and have webbed feet adapted for swimming, while tortoises are land-dwelling reptiles with feet suited for walking on land.
Turtles and tortoises are fascinating creatures that have captured the imagination of humans for centuries. As a professional author, I have always been intrigued by these unique reptiles and their distinct characteristics. Turtles and tortoises belong to the same family, Testudines, but they have some notable differences that set them apart.
It is important to know the difference between turtles and tortoises because they have different physical attributes, habitats, diets, behaviors, and even reproductive processes. Understanding these distinctions allows us to appreciate their individual qualities better and contribute to their conservation efforts.
Key Takeaways
- Turtles and tortoises are two different types of reptiles with distinct physical and behavioral differences.
- Turtles have webbed feet and are adapted for swimming, while tortoises have stumpy feet and are adapted for walking on land.
- Turtles and tortoises have different habitats and distributions, with turtles found in aquatic environments and tortoises found on land.
- Turtles and tortoises have different diets and feeding habits, with turtles being omnivores and tortoises being herbivores.
- Turtles and tortoises play important roles in ecosystems, but are threatened by habitat loss, pollution, and other human activities, making conservation efforts crucial.
Physical Differences between Turtles and Tortoises
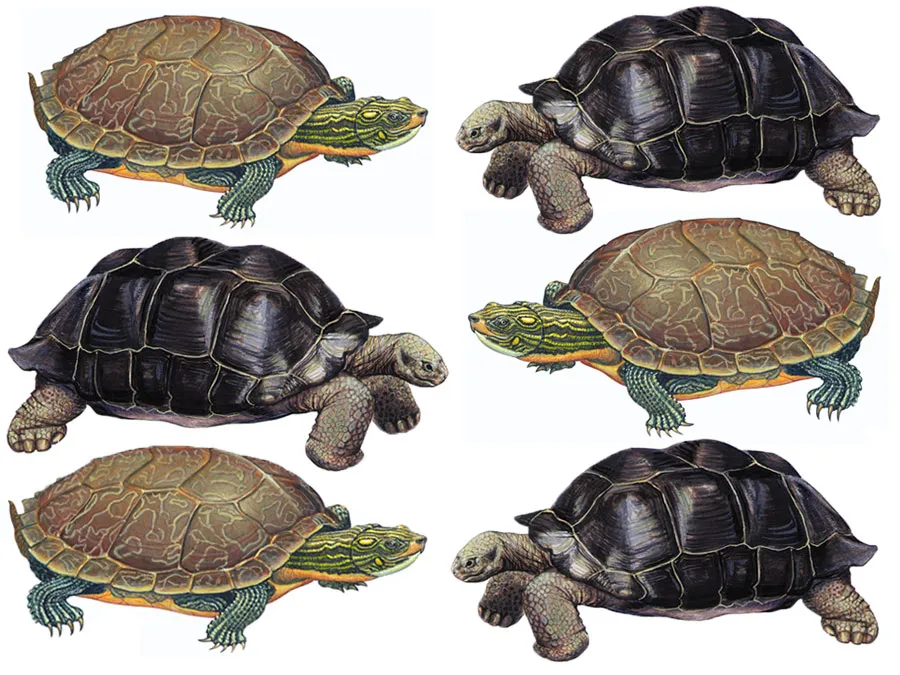
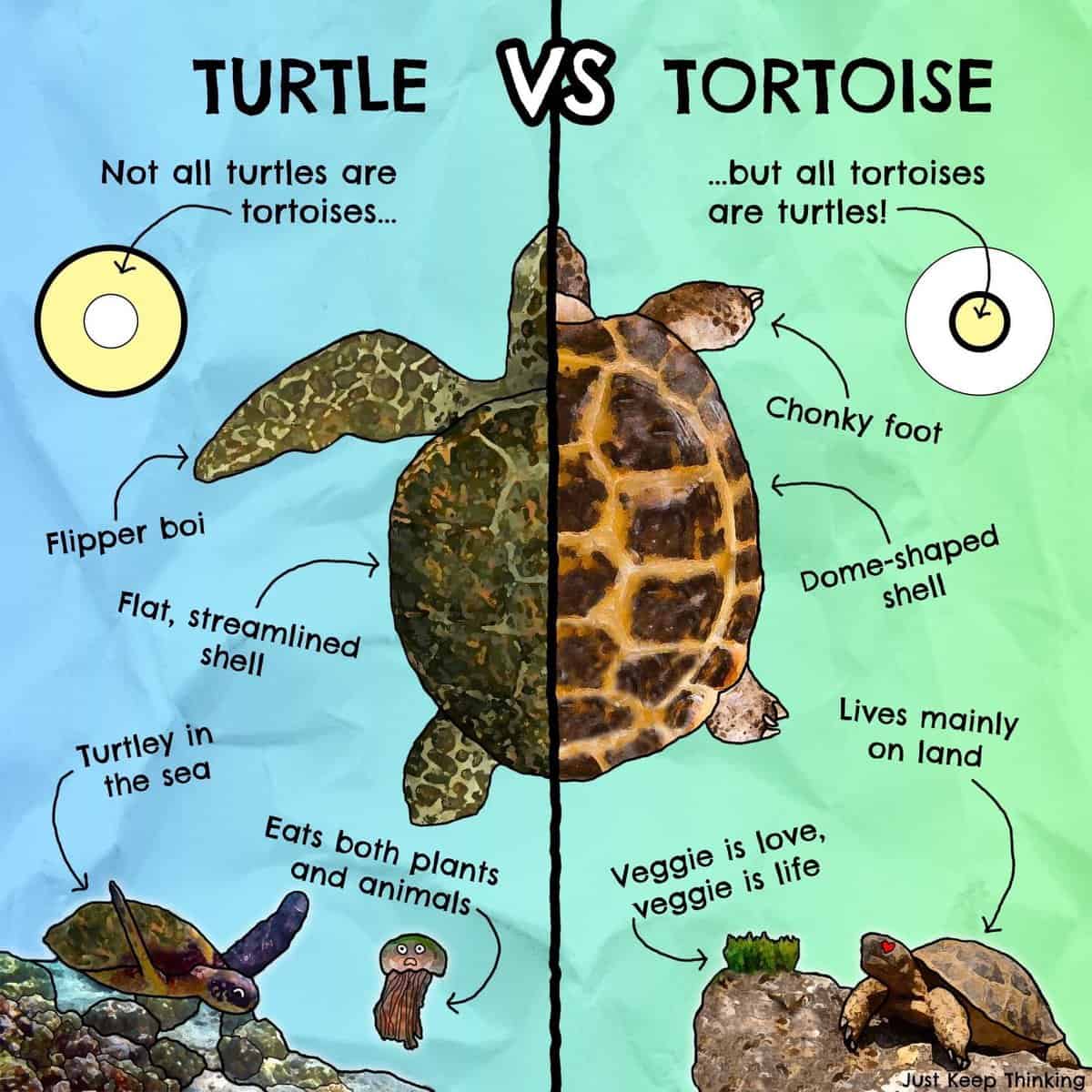
One of the most apparent differences between turtles and tortoises lies in their shell shape and size. Turtles typically have streamlined shells that are designed for swimming in water bodies like rivers or oceans. On the other hand, tortoises possess domed shells that provide protection against predators on land.
Another distinguishing feature is their limb structure. Turtles usually have webbed feet or flippers adapted for swimming through water currents effortlessly. In contrast, tortoises possess sturdy legs with claws suitable for walking on land or digging burrows.
Furthermore, turtles tend to have a more streamlined head shape with a pointed snout compared to the rounder heads of tortoises. Additionally, turtle necks are longer than those of tortoises since they need flexibility while hunting underwater prey.
Habitat and Distribution of Turtles and Tortoises
Turtles can be found in various habitats worldwide such as freshwater lakes, rivers, swamps as well as oceans across all continents except Antarctica. They are highly adaptable creatures capable of thriving in diverse environments ranging from tropical rainforests to arid deserts.
On the other hand, tortoise species primarily inhabit terrestrial ecosystems like grasslands or deserts where they can find ample vegetation for sustenance. They are often found in specific regions such as the Galapagos Islands, the Mojave Desert, or the African savannah.
Diet and Feeding Habits of Turtles and Tortoises
| Turtle/Tortoise Species | Diet | Feeding Habits |
|---|---|---|
| Red-eared Slider | Vegetation, insects, fish, and small aquatic animals | Active foragers, opportunistic feeders |
| Box Turtle | Vegetation, insects, snails, and worms | Slow and deliberate feeders, may bury food for later consumption |
| Green Sea Turtle | Seagrass, algae, and jellyfish | Herbivorous grazers, may migrate long distances to feeding grounds |
| Gopher Tortoise | Grasses, legumes, and succulent plants | Diurnal grazers, may store food in burrows for later consumption |
Turtles have a more omnivorous diet compared to tortoises. They consume a variety of food sources including plants, insects, fish, and even small mammals. Some turtle species are known to be opportunistic feeders, taking advantage of whatever food is available in their environment.
In contrast, tortoises are primarily herbivores with a diet consisting mainly of grasses, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Their strong jaws allow them to chew tough vegetation efficiently. This specialized feeding habit is due to their adaptation for life on land where plant matter is more abundant than animal prey.
Reproduction and Life Cycle of Turtles and Tortoises
The reproductive processes of turtles and tortoises also differ significantly. Turtles typically lay their eggs in sandy areas near bodies of water where they can hatch safely after an incubation period ranging from several weeks to months depending on the species.
Tortoises have a similar egg-laying process but tend to dig deeper nests since they rely solely on terrestrial environments for reproduction. The incubation period for tortoise eggs can be longer than that of turtles due to differences in environmental conditions.
Behavioral Differences between Turtles and Tortoises
When it comes to behavior, turtles tend to be more active creatures compared to their slower-moving counterparts – the tortoises. Turtles spend much of their time swimming or basking under the sun while exploring their aquatic habitats.
On the other hand, tortoises are known for their slow movements on land due to their heavy shells which provide protection against predators but limit agility as well. They spend most of their time grazing on vegetation or seeking shelter from extreme temperatures by burrowing into the ground.
Communication methods also differ between turtles and tortoises. Turtles use a combination of visual cues, body language, and vocalizations to communicate with each other. Tortoises, however, rely more on non-verbal communication such as hissing or head-bobbing to establish dominance or attract mates.
Importance of Turtles and Tortoises in Ecosystems
Turtles and tortoises play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of ecosystems they inhabit. As predators, turtles help control populations of small aquatic animals like fish or insects, preventing overpopulation that could disrupt the food chain.
Moreover, tortoises contribute to plant growth by dispersing seeds through their feces as they move around their habitats. This process aids in the regeneration of vegetation and helps maintain biodiversity within their ecosystems.
Furthermore, these reptiles hold cultural significance for many societies around the world. They have been revered as symbols of longevity, wisdom, and resilience in various cultures throughout history.
Threats to Turtles and Tortoises and Conservation Efforts
Unfortunately, turtles and tortoises face numerous threats from human activities that harm their populations worldwide. Habitat destruction due to urbanization or deforestation is one significant threat they encounter regularly.
Additionally, illegal wildlife trade poses a severe threat to these reptiles as they are often captured for exotic pet markets or used for traditional medicine purposes in some cultures.
To combat these threats effectively, conservation efforts have been implemented globally. These initiatives focus on habitat protection measures such as establishing protected areas where turtles and tortoises can thrive undisturbed by human activities.
Popular Turtle and Tortoise Species
There are numerous turtle species known for their unique characteristics across different regions worldwide. The Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas) is one well-known species famous for its migratory behavior between feeding grounds and nesting beaches across oceans.
Another popular turtle species is the Red-Eared Slider (Trachemys scripta elegans), often kept as a pet due to its vibrant appearance and relatively small size compared to other turtle species.
As for tortoises, the Galapagos Tortoise (Chelonoidis nigra) stands out as one of the most iconic species due to its enormous size and long lifespan. These tortoises can live for over a hundred years, making them living relics of evolutionary history.
Keeping Turtles and Tortoises as Pets: What You Need to Know
Keeping turtles and tortoises as pets requires careful consideration of their specific needs. It is essential to research local laws regarding pet ownership since some species may be protected or require special permits.
Providing appropriate housing is crucial, with ample space for both land-dwelling and aquatic turtles. Enclosures should mimic their natural habitats, including UVB lighting for proper calcium absorption.
Feeding requirements vary depending on the species, but it is generally recommended to offer a balanced diet consisting of commercial turtle pellets supplemented with fresh vegetables or fruits.
Regular veterinary check-ups are necessary to ensure the health and well-being of these reptiles. Common health concerns include respiratory infections, shell injuries, or nutritional deficiencies that can be addressed through proper care and diet management.
Appreciating the Unique Qualities of Turtles and Tortoises
In conclusion, turtles and tortoises are remarkable creatures that deserve our appreciation and protection. Understanding their physical differences, habitats, diets, behaviors, reproductive processes allows us to develop a deeper connection with these unique animals.
By recognizing their importance in ecosystems as well as cultural significance worldwide, we can contribute towards conservation efforts aimed at preserving these incredible reptiles for future generations.
Let us embrace the beauty of turtles’ graceful swimming in oceans or marvel at the resilience of tortoises slowly traversing arid landscapes – each showcasing nature’s ingenuity in creating such diverse creatures within the Testudines family.
FAQs
What is the difference between a turtle and a tortoise?
Turtles and tortoises are both reptiles, but they belong to different families. Turtles are aquatic or semi-aquatic, while tortoises are land-dwelling.
How can you tell a turtle from a tortoise?
One way to tell the difference is by looking at their feet. Turtles have webbed feet with long claws, while tortoises have short, stumpy feet with thick, round toes. Additionally, turtles have a more streamlined, flat shell, while tortoises have a dome-shaped shell.
Do turtles and tortoises have different diets?
Yes, turtles and tortoises have different diets. Turtles are omnivores and eat both plants and animals, while tortoises are herbivores and eat only plants.
Where do turtles and tortoises live?
Turtles can be found in a variety of aquatic habitats, such as ponds, lakes, and oceans. Tortoises, on the other hand, are found in dry, arid regions such as deserts and grasslands.
Can turtles and tortoises interbreed?
No, turtles and tortoises cannot interbreed because they belong to different families.
Originally posted 2024-02-07 04:23:03.