Tortoises can sense pressure and pain on their shell’s outer layer, called the carapace, due to nerves and blood vessels present, though they do not have the same sensory capabilities as skin.
Cracking the Code: Understanding Tortoise Sensations in Their Shell
Tortoises are fascinating creatures that have captured the curiosity of humans for centuries. One of the most intriguing aspects of tortoises is their shell, which serves as their home and a vital part of their survival. Understanding tortoise behavior and how they sense their environment through their shell is crucial for their well-being and conservation efforts.
The Importance of Understanding Tortoise Behavior
Tortoise behavior is closely linked to their shell, as it plays a significant role in their survival. The shell provides protection from predators and harsh environmental conditions, making it essential for their survival in the wild. By understanding tortoise behavior, researchers and conservationists can develop strategies to protect these magnificent creatures and ensure their long-term survival.
The Anatomy of a Tortoise Shell
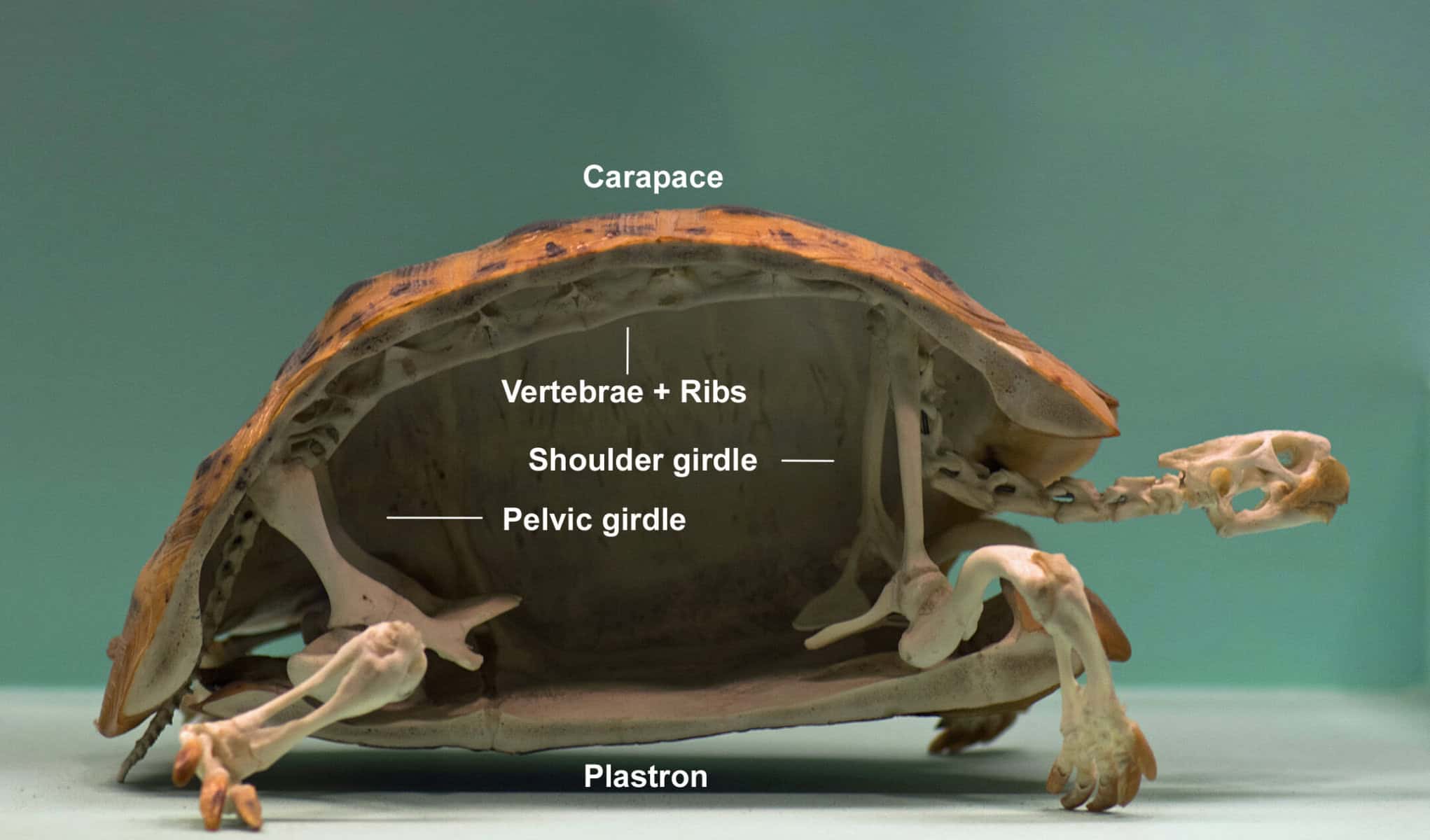
A tortoise shell is composed of two main parts: the carapace and the plastron. The carapace is the upper part of the shell, which covers the tortoise’s back, while the plastron is the lower part that covers its belly. These two parts are connected by a bridge called the bridge bone.
The shell is formed by a combination of bone and keratin, a tough protein found in hair and nails. As a tortoise grows, its shell grows with it, thanks to specialized cells called osteoblasts that continuously produce new bone tissue. This growth allows the tortoise to adapt to its changing size and environment.
How Tortoises Use Their Shell for Protection
Tortoises use their shell for protection in various ways. When threatened, they can retract their head, legs, and tail into their shell, creating a secure hiding place. The shell acts as a shield against predators, providing a strong barrier that is difficult to penetrate.
Additionally, tortoises can use their shell as camouflage by blending in with their surroundings. Some species have shells that resemble rocks or vegetation, allowing them to hide from predators and remain undetected.
The Different Types of Tortoise Shells
Tortoise shells come in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on the species. Some species have domed shells, while others have flatter shells. The shape of the shell can provide clues about the tortoise’s habitat and behavior.
For example, tortoises with domed shells are often found in areas with tall grass or dense vegetation, where they need to navigate through obstacles. On the other hand, tortoises with flatter shells are typically found in open habitats, where they need to move quickly and efficiently.
The Science Behind Tortoise Sensations in Their Shell
Tortoises are able to sense their environment through their shell, thanks to a network of nerves that run throughout its surface. These nerves allow them to feel pressure, temperature, and even pain.
The shell is covered in a layer of skin called the scutes, which are made up of keratin. Beneath the scutes are sensory receptors that detect changes in pressure and temperature. When a tortoise comes into contact with an object or surface, these receptors send signals to its brain, allowing it to perceive its surroundings.
The Nervous System of a Tortoise
The nervous system of a tortoise is responsible for coordinating its behavior and responses to stimuli. It consists of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves that extend throughout the body.
The brain processes sensory information received from the shell and other parts of the body, allowing the tortoise to make decisions and respond accordingly. The spinal cord acts as a communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body, transmitting signals back and forth.
How Tortoises Sense Their Environment Through Their Shell
Tortoises sense their environment through their shell in several ways. One way is through touch, as the shell is covered in sensory receptors that can detect changes in pressure. When a tortoise comes into contact with an object or surface, these receptors send signals to its brain, allowing it to perceive its surroundings.
Tortoises can also sense temperature through their shell. The shell acts as a thermal conductor, allowing the tortoise to detect changes in temperature and regulate its body heat accordingly. This ability is crucial for their survival, as it helps them maintain optimal body temperature in different environments.
The Role of Temperature in Tortoise Sensations
Temperature plays a vital role in tortoise sensations in their shell. Tortoises are ectothermic animals, which means they rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. The shell acts as a thermal conductor, allowing the tortoise to absorb heat from its surroundings and warm up.
Tortoises can also cool down by seeking shade or burrowing into the ground. The shell helps insulate the tortoise’s body, preventing excessive heat loss or gain. This ability to regulate body temperature is crucial for their overall health and well-being.
Common Misconceptions About Tortoise Shells
There are several common misconceptions about tortoise shells that need to be debunked. One misconception is that a tortoise can completely retract into its shell. While tortoises can retract their head, legs, and tail into their shell for protection, they cannot retract their entire body.
Another misconception is that a tortoise’s shell is detachable. In reality, the shell is fused to the tortoise’s skeleton and cannot be removed without causing severe harm or death.
The Future of Tortoise Research and Conservation
Understanding tortoise behavior and sensations in their shell is crucial for their conservation. By studying how tortoises use their shell for protection and sense their environment, researchers and conservationists can develop strategies to protect these magnificent creatures and their habitats.
Conservation efforts should focus on preserving tortoise habitats, implementing laws and regulations to prevent illegal trade and poaching, and raising awareness about the importance of these creatures in their ecosystems. Continued research and conservation efforts are essential to ensure the long-term survival of tortoises and their unique behaviors.
Tortoises are remarkable creatures with a unique shell that plays a vital role in their survival. Understanding tortoise behavior and how they sense their environment through their shell is crucial for their well-being and conservation efforts. By studying the anatomy of a tortoise shell, the science behind tortoise sensations, and the role of temperature in their sensations, we can gain a deeper appreciation for these magnificent creatures and work towards their protection and conservation.
Originally posted 2024-02-08 09:37:46.